3D Printing
As 3D printing for prototyping becomes increasingly common, various technologies and methods have emerged, each tailored to specific needs.
Some of the most popular methods include:
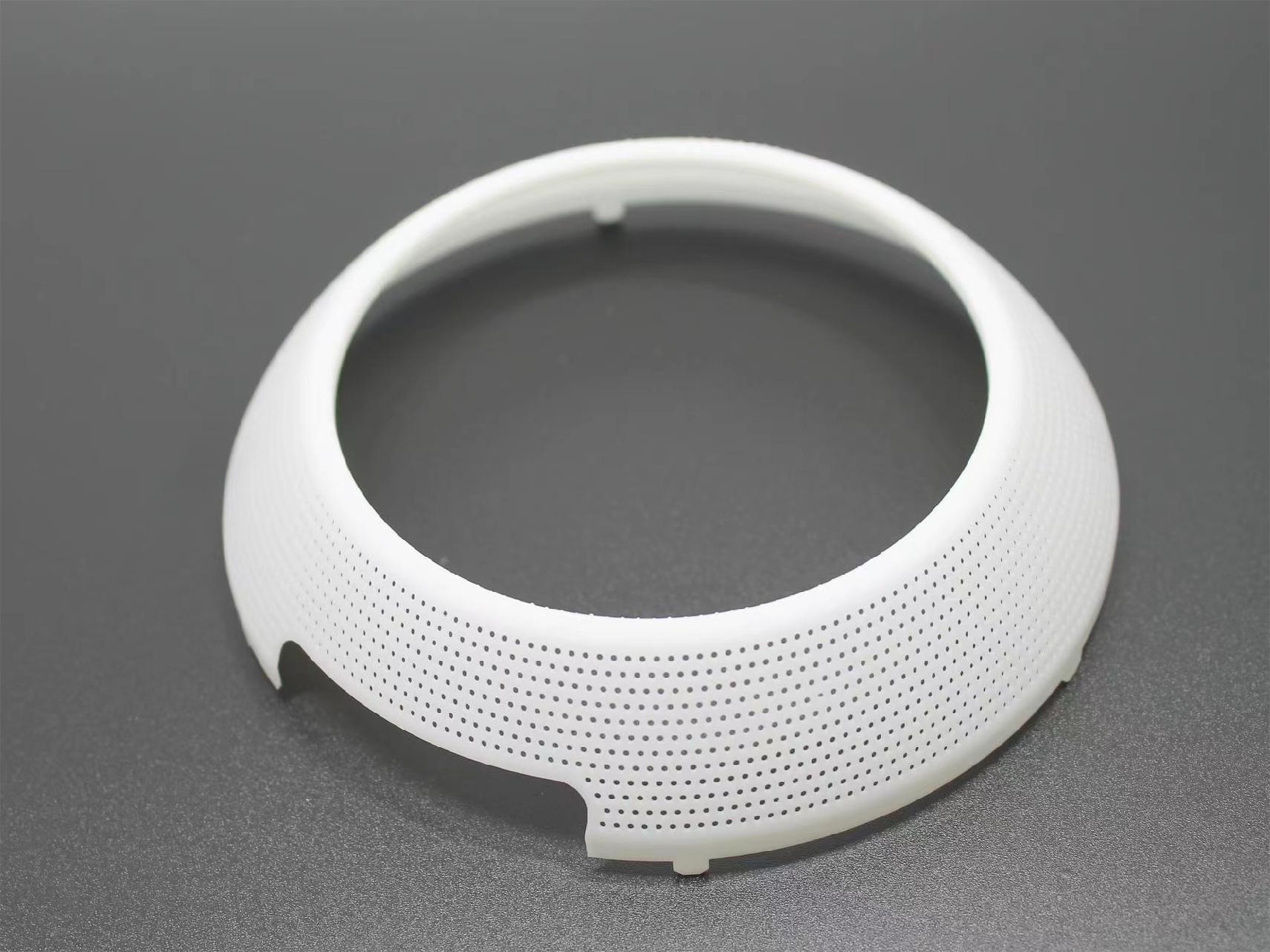
• SLA: One of the earliest technologies used for prototyping in 3D printing, involving the use of a laser to selectively solidify liquid resin layer by layer.
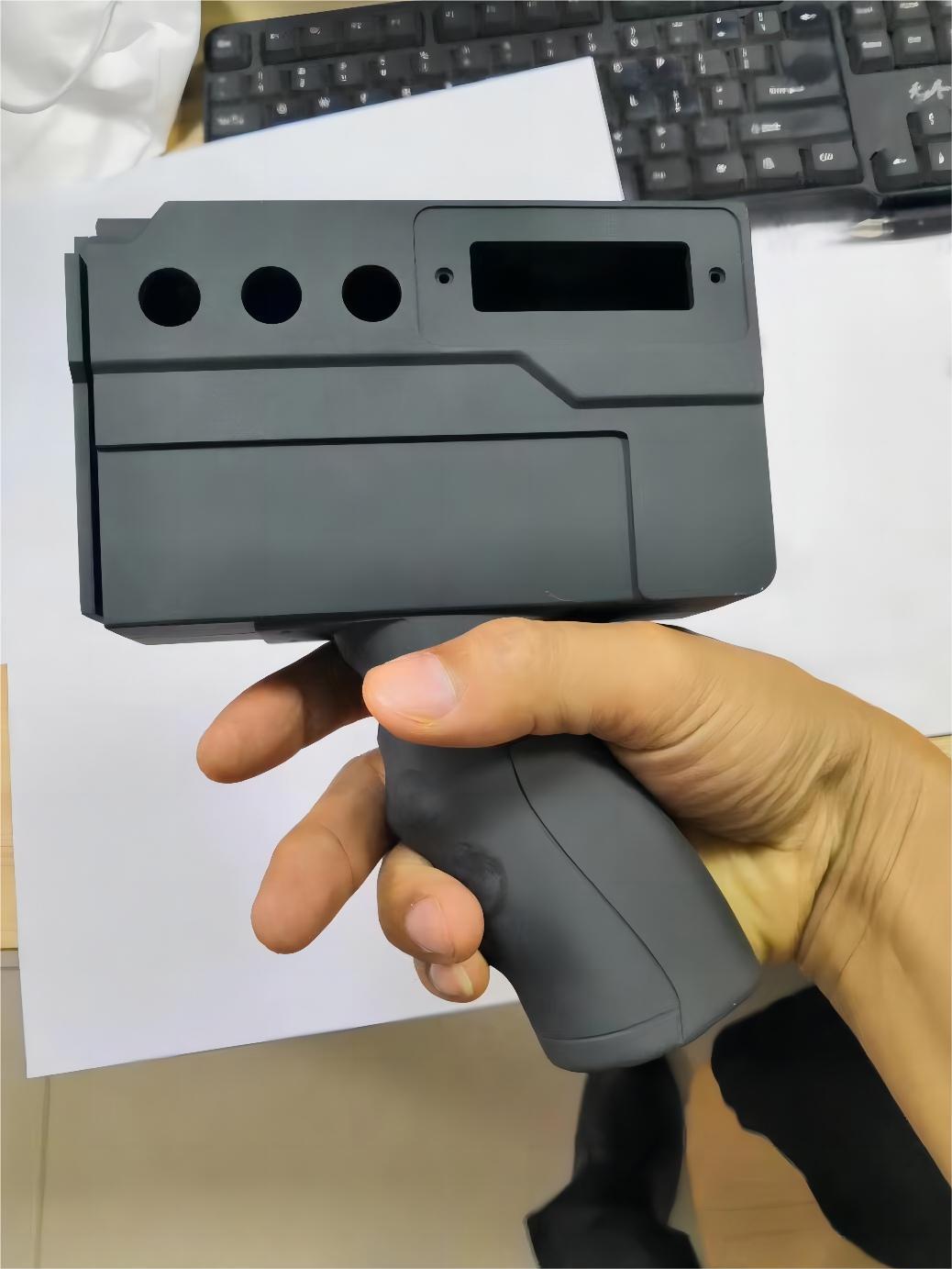
• FDM: In the realm of prototype 3D printing, FDM is a method that builds objects layer by layer by extruding material through a heated nozzle. It is particularly suited for producing larger parts.
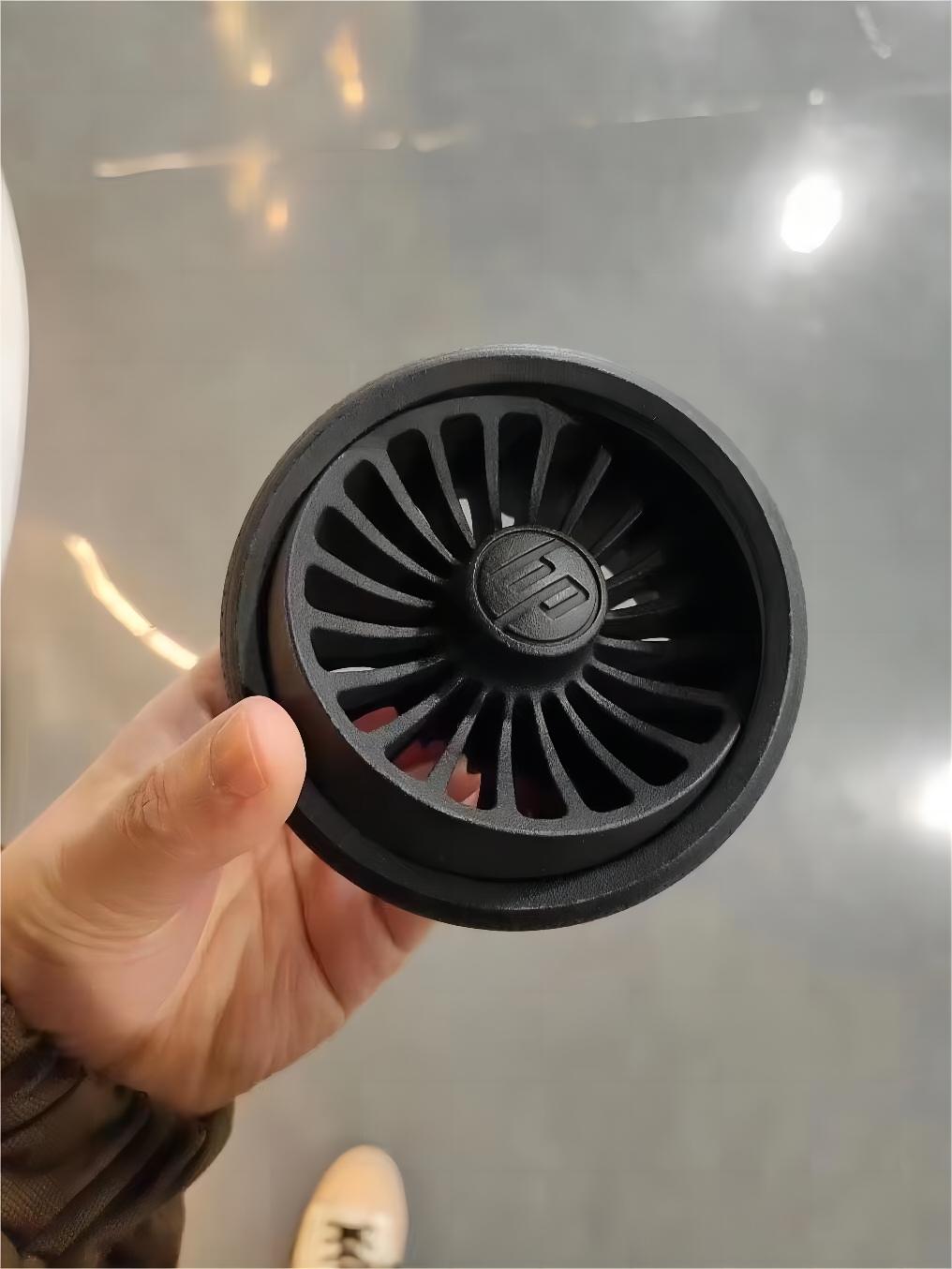
• SLS: An important technology for prototyping in 3D printing, this method involves using a laser to fuse powdered materials (such as nylon or metal) into solid structures. Given its ability to produce high-strength parts, SLS has significant utility in automotive applications.
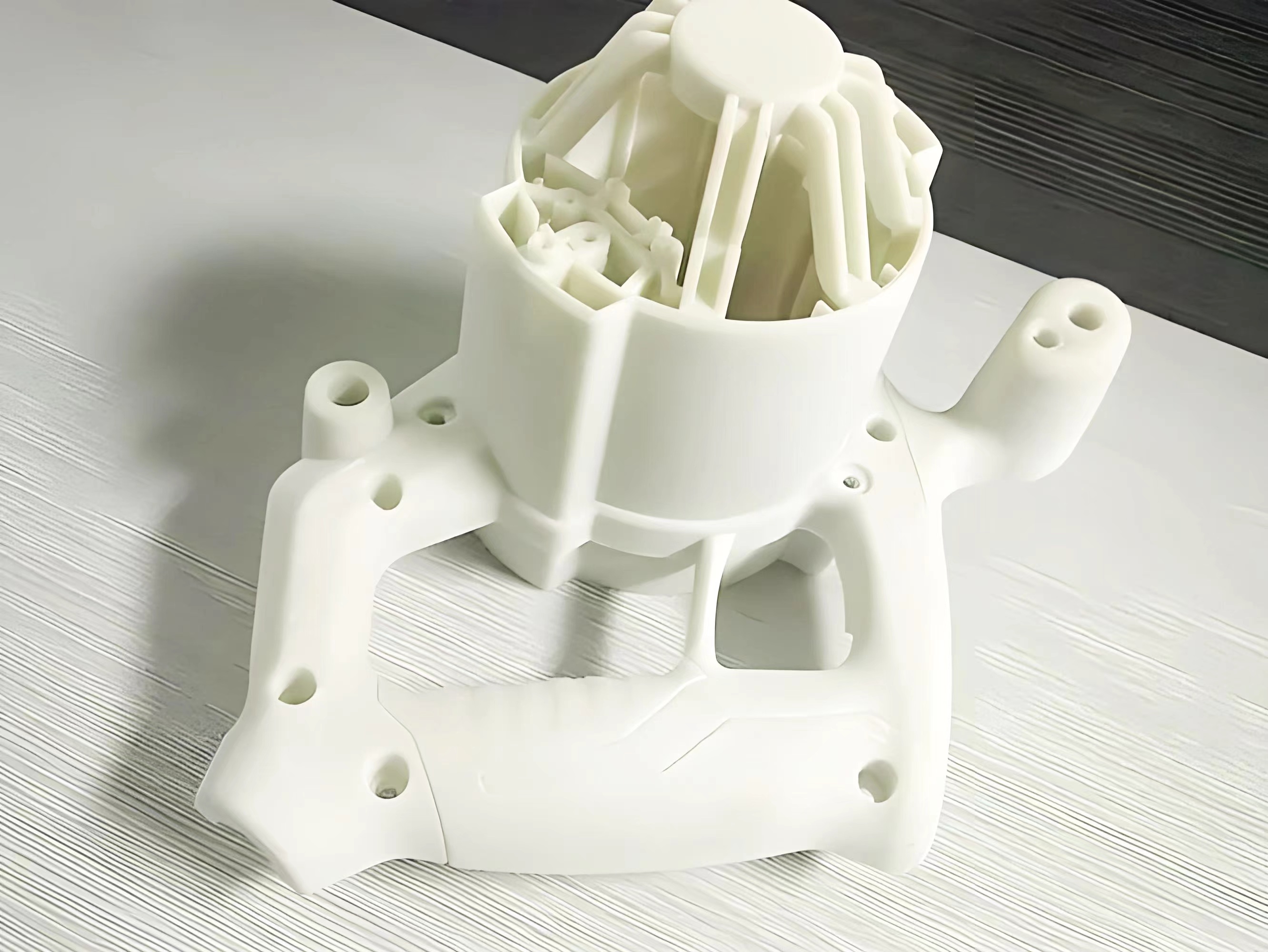
• Metal 3D Printing: In the context of prototype 3D printing, parts requiring high strength and durability can be manufactured using metal 3D printing.
Technologies like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) play a crucial role in fabricating complex metal components for high-performance vehicles.
The choice of technology largely depends on the purpose of the prototype, the required materials, and the durability needed for the parts.
Regardless of the method chosen, the essence remains consistent: 3D printing offers a fusion of unprecedented speed, flexibility, and precision, solidifying its position as a cornerstone for future automotive design and manufacturing.