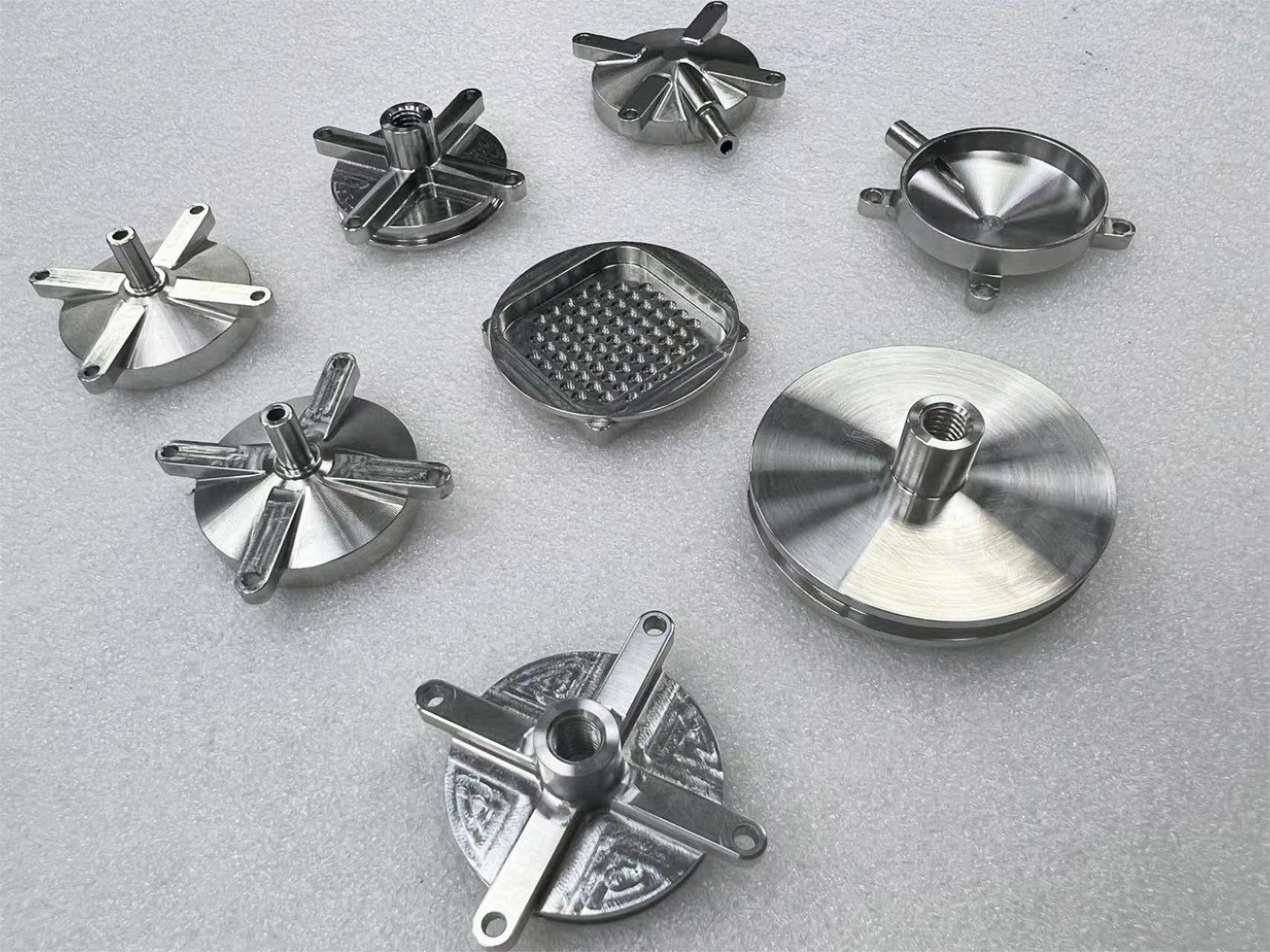
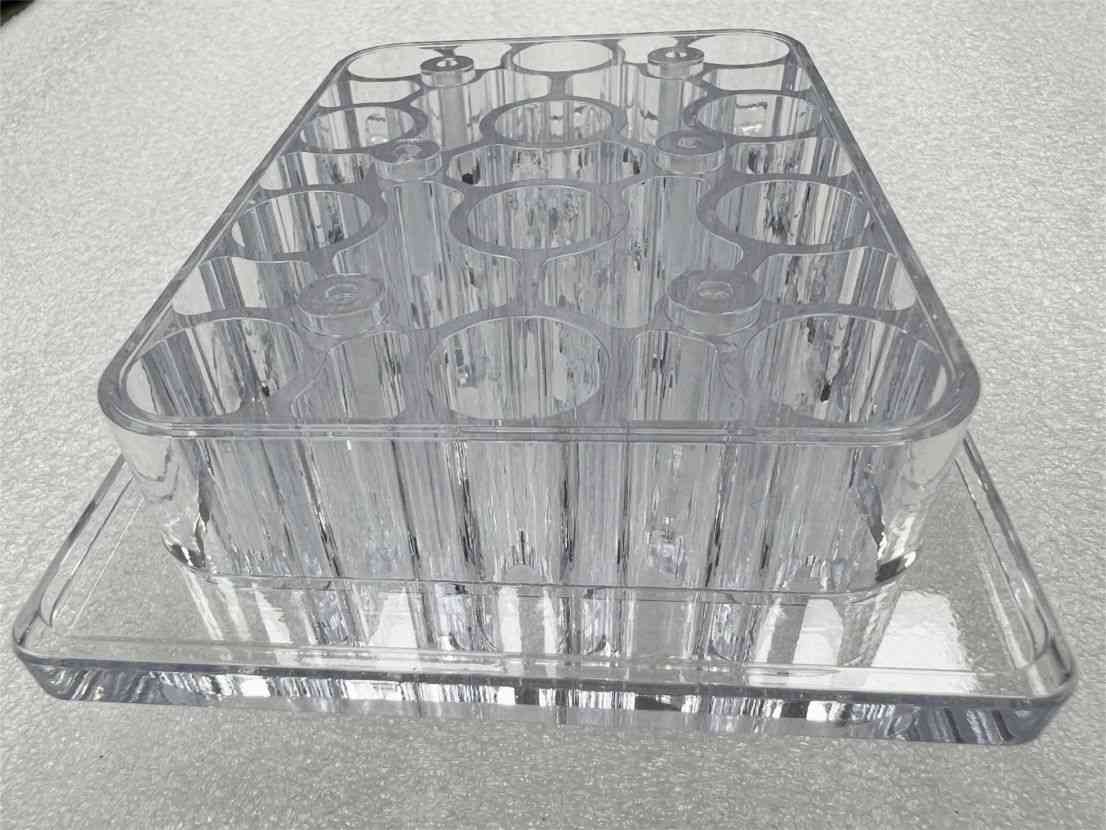
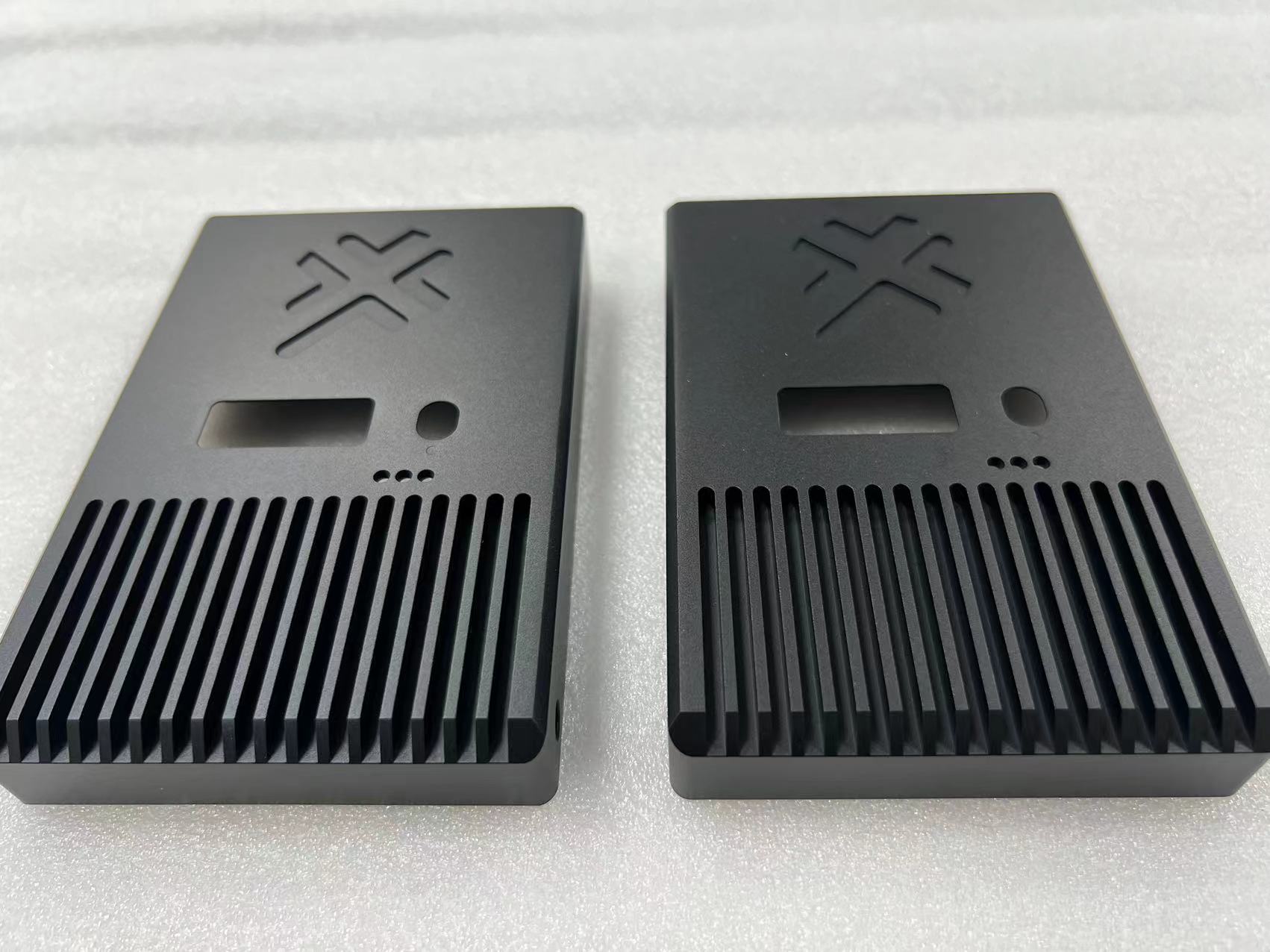
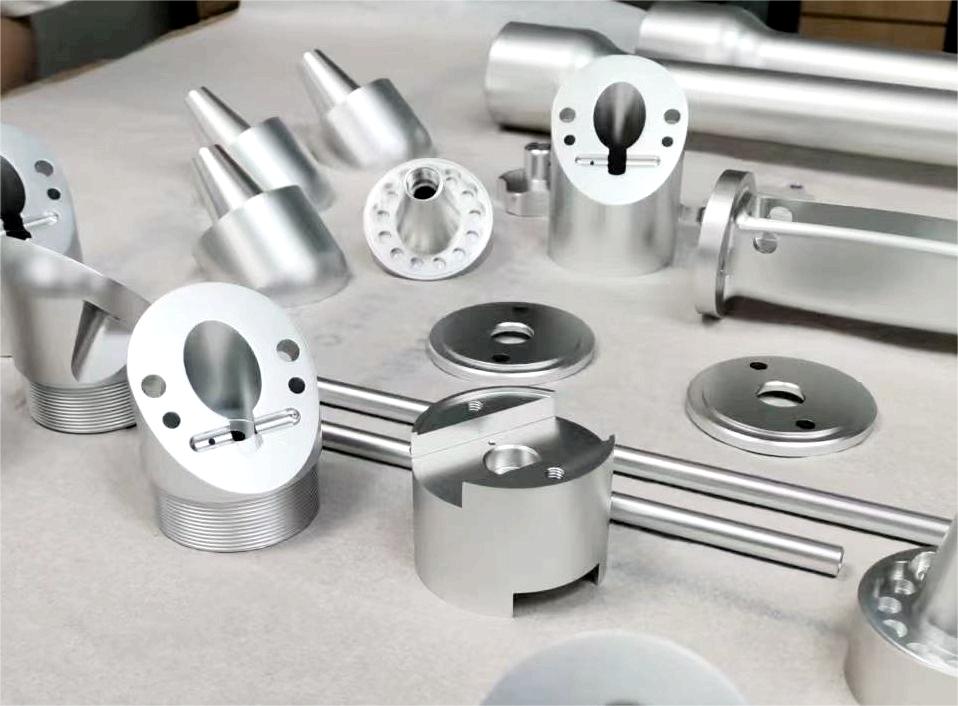
Stainless steel parts
Heat Treatment of Stainless Steel and Steel
Heat treatment refers to several different processes involving manipulation of the temperature of steel to alter its material properties.
Annealing is used to reduce hardness and increase ductility, making the steel easier to work with.
The annealing process involves slowly heating the steel to the desired temperature and holding it there for a period of time.
The required time and temperature depend on the specific alloy and decrease with increasing carbon content. Finally, the steel is slowly cooled in the furnace or surrounded by insulating material.
Normalizing can relieve internal stresses in the steel while maintaining higher strength and hardness compared to annealed steel.
In the normalizing process, the steel is heated to a high temperature and then cooled at a suitable rate to improve its hardness.
Quenching not only hardens the steel but also increases its strength, although it can make it more brittle.
The hardening process involves slowly heating the steel, soaking it at a high temperature, and then rapidly cooling it by immersing it in water, oil, or a brine solution.
Tempering can be used to reduce some of the brittleness caused by steel hardening.
Tempering steel is almost identical to normalizing: it is first slowly heated to the selected temperature and then air-cooled.
The difference is that tempering is done at lower temperatures than other processes, which reduces the brittleness and hardness of tempered steel.